Blog

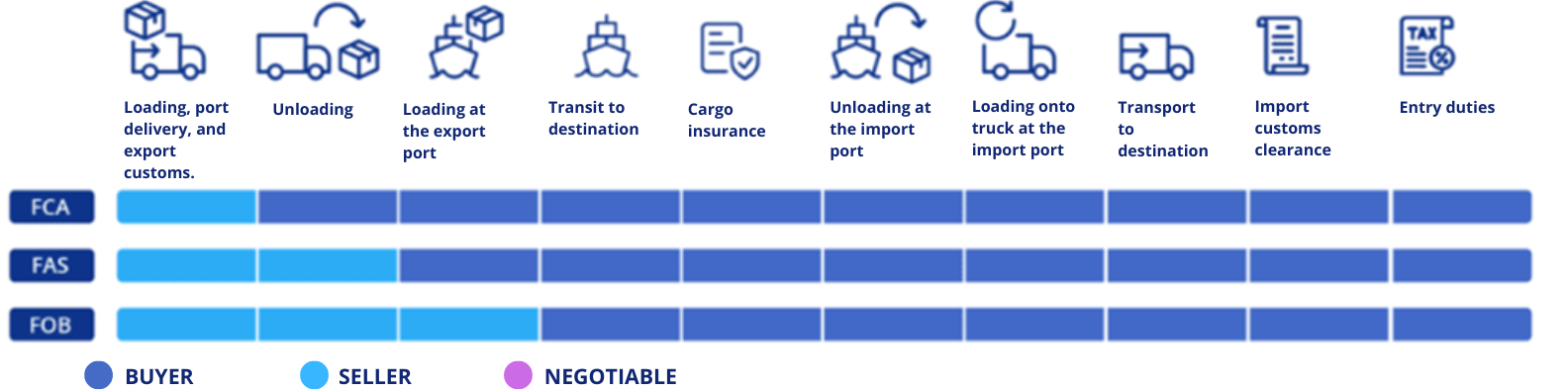
GROUP F: The costs and risks of the main transportation are the responsibility of the buyer.
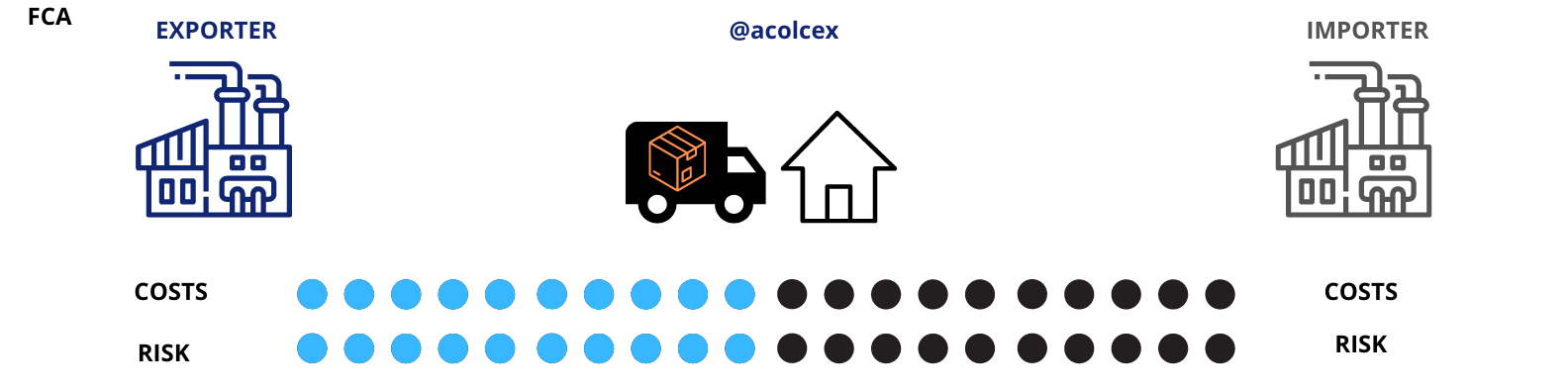
FCA: Free Carrier
FAS: Free Alongside Ship
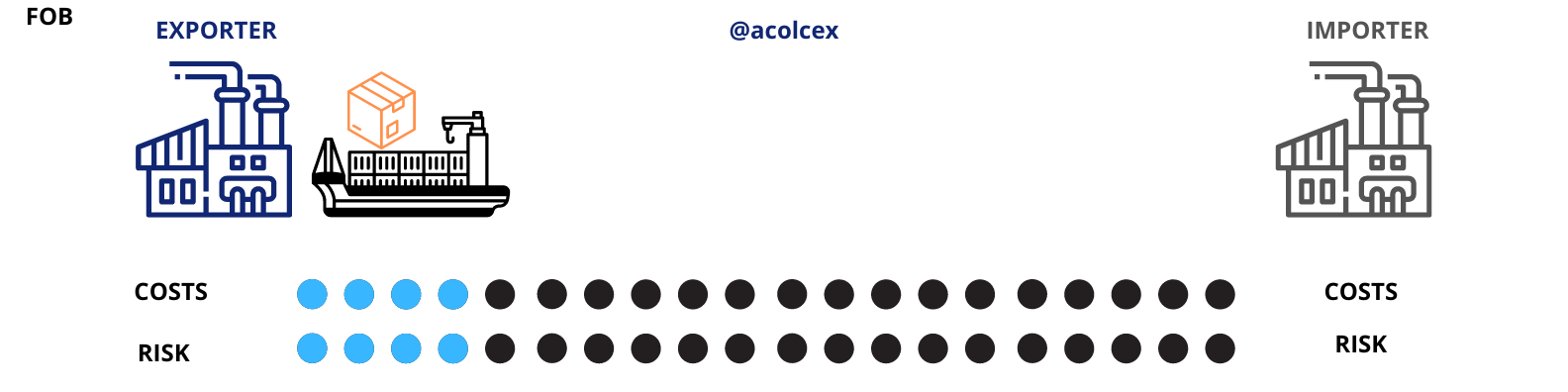
FOB: Free On Board
INCOTERM FCA
Incoterms, international trade terms, are essential for establishing responsibilities and costs in international transactions. One of the most commonly used terms is "Free Carrier" (FCA), which specifies obligations for both the seller and the buyer in a transaction. We will delve into the Incoterm FCA, highlighting its key aspects.
Under the Incoterm FCA, the seller fulfills their responsibility by delivering the goods to the designated carrier or another person indicated by the buyer at the agreed-upon place, either in the seller's own country or at an agreed-upon point at the border.
From that moment on, the buyer assumes the costs and risks, including those related to the main transportation, loading, and export customs clearance.
What is the Incoterm FCA?
The Incoterm FCA, or "Free Carrier," establishes that the seller fulfills their delivery obligation when they deliver the goods, cleared for export, to the carrier designated by the buyer at an agreed-upon place. Here, we break down the responsibilities of the seller and the buyer:
Seller's Obligations:
Goods Delivery: The seller must deliver the goods at the agreed-upon location, whether at their premises or another agreed-upon place.
Customs Clearance: The seller is responsible for export procedures and customs clearance.
Documentation: They must provide all necessary documentation, either in physical or electronic form.
Packaging Terms: The seller must pack, inspect quality and quantity, and ensure all necessary details for the product to be transported.
Loading and Unloading: The seller must deliver the goods at the specified location and load them onto the transportation means defined by the buyer.
Insurance: While the merchandise is in transit, the buyer may request assistance in acquiring insurance. However, since the risk lies with the buyer, the costs must be covered by them without involving the seller.
Costs: They must cover costs related to delivering the goods at the designated site; all taxes and fees from the export procedure or the issuance of necessary documentation.
Buyer's Obligations:
Loading and Unloading: The buyer assumes responsibility for loading and unloading the goods at the agreed-upon place of delivery.
Import Costs: Costs associated with importing the goods, including taxes and tariffs, are the buyer's responsibility.
Packaging Terms: The buyer has no obligation regarding the packaging of goods in terms of quality or process.
Delivery Terms: A delivery location is determined, either the seller's warehouse or factory, as well as another defined point, in which case the costs and responsibility up to that location are covered by the seller.
Insurance: From the delivery, costs and risks are transferred to the buyer, so there is no obligation to acquire insurance. However, they may agree to insure the merchandise, but it will be the buyer's responsibility.
Advantages:
Flexibility: It offers flexibility by allowing delivery to various locations.
Clear Costs: It clearly defines responsibilities and associated costs.
Disadvantages:
Logistical Complexity: The need to coordinate delivery in various locations can increase logistical complexity.
Potential Disagreements: Determining the exact delivery location may lead to disagreements between parties.
Associated Risks:
Transport Risks: Until the merchandise is in the hands of the carrier, the risk lies with the seller.
Customs Risks: Customs risks in the country of origin are the seller's responsibility.
Legal Considerations:
Detailed Contract: Having a detailed contract that clearly specifies the responsibilities of both parties is crucial.
Cargo Insurance: It is recommended that the buyer obtains cargo insurance to cover potential losses or damages during transportation.
Conclusions:
In summary, the FCA Incoterm offers flexibility and clarity in international transactions, but its effective use requires detailed understanding and open communication between parties. By establishing a clear contract and properly managing risks, both sellers and buyers can benefit significantly from this international trade term.
INCOTERM FAS
FAS: Free Alongside Ship
Incoterms are an essential component in international trade, and among them stands out the "Free Alongside Ship" (FAS). In this blog, we will break down the key characteristics of the FAS Incoterm, examining the responsibilities of the seller and the buyer, its advantages, disadvantages, risks, legal considerations, and how to use it effectively.
What Does FAS Imply?
"Free Alongside Ship" indicates that the seller fulfills their delivery obligation when they place the merchandise alongside the ship (or on a raft or barge), already cleared for export, at the designated port of shipment.

Seller's Obligations:
Goods Delivery: The seller must place the goods alongside the ship at the designated port of shipment.
Customs Clearance for Export: It is the seller's responsibility to carry out customs clearance for export.
Loading and Unloading: While the seller must handle the loading of the goods onto their own vessel, loading onto the buyer's ship is the responsibility of the importer.
Cost: Until delivery, the costs borne by the seller include packaging, loading charges, and transportation before reaching the destination vessel, as well as associated export fees.
Insurance: The exporter has no obligation regarding insurance acquisition. Even if they undertake the process, the obligation to cover it lies with the buyer.
Buyer's Obligations:
Loading Costs: The buyer assumes the costs and risks associated with loading the goods onto the ship.
Import Costs: All costs related to importation, including taxes and tariffs, are the buyer's responsibility.
Loading and Unloading: Loading onto the destination vessel depends on the buyer.
Delivery and Freight Terms: Once the seller delivers the goods onto the buyer's vessel, delivery to the final destination or warehouse is entirely the buyer's responsibility.
Insurance: It is up to the buyer to cover the risks assumed in transporting the goods, both on land and by sea.
Customs Clearance: Import procedures into the final country are the buyer's responsibility, including costs and fees to be paid.
Advantages:
Buyer Control: The buyer has control over loading the goods onto the ship.
Clarity in Responsibilities: Clearly defines the responsibilities of both parties.
Disadvantages:
Limited for Containers: Not suitable for goods transported in containers, as it involves loading alongside the ship.
Logistical Complexity: The need to coordinate loading at the port can increase logistical complexity.
Associated Risks:
Loading Risks: Risks associated with loading the goods onto the ship are the buyer's responsibility.
Maritime Transport Risks: Risks during maritime transportation fall on the buyer.
Legal Considerations:
Detailed Documentation: Accurate documentation is essential to avoid misunderstandings and disputes.
Cargo Insurance: It is recommended that the buyer obtain cargo insurance to cover losses or damages during transportation.
Conclusions:
In conclusion, the FAS Incoterm offers a solid framework for international transactions, especially those related to maritime transportation. By understanding responsibilities, carefully addressing risks, and using it appropriately, companies can optimize their international business operations for continued success in the global market. Use the FAS Incoterm strategically to boost your international presence!
INCOTERM FOB
FOB: Free On Board
Incoterms are an essential guide in the world of international trade, and one of the most used terms is "Free On Board" (FOB). In this blog, we will delve into what the FOB Incoterm entails, examining in detail the obligations of the seller and the buyer, responsibilities, advantages, disadvantages, risks, legal aspects, and how to effectively employ this term.
What Does FOB Mean?
"Free On Board" indicates that the seller fulfills their delivery obligation when the merchandise passes onto the ship at the designated port of shipment.